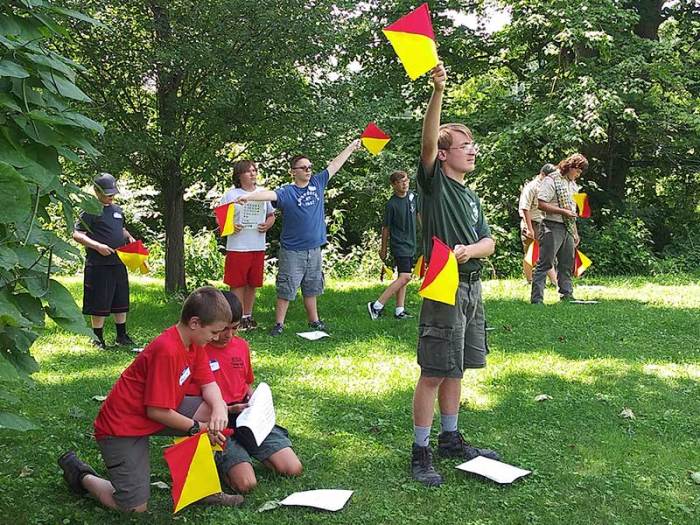
Signs, signals, and codes merit badge – Delving into the fascinating realm of communication, we embark on a journey to explore the enigmatic world of Signs, Signals, and Codes. From ancient origins to modern-day applications, this merit badge unravels the intricate tapestry of how we convey messages across vast distances and diverse situations.
Unveiling the secrets of nonverbal communication, we delve into the history, types, and methods employed in sending and receiving signs, signals, and codes. Discover the ethical considerations that guide their responsible use, the skills required to master this art, and the resources available for further exploration.
Define Signs, Signals, and Codes
Within the context of the Signs, Signals, and Codes merit badge, these terms refer to distinct methods of communication:
Signsare physical objects or gestures that convey specific meanings. They can be static, like traffic signs, or dynamic, like hand gestures.
Signals
Signalsare patterns of light, sound, or other stimuli that transmit information. They can be used over long distances, like Morse code, or short distances, like a smoke signal.
Codes
Codesare systems of symbols that represent words or ideas. They can be used to encrypt messages, like the Enigma code, or to create secret languages, like pig Latin.
History of Signs, Signals, and Codes
Communication through signs, signals, and codes has a long and fascinating history, dating back to the earliest forms of human interaction. The need to convey information across distances and overcome language barriers has driven the development of a wide range of communication systems.
Origins and Evolution
The origins of signs and signals can be traced to prehistoric times, when humans used simple gestures, body language, and smoke signals to communicate with each other. As civilizations developed, the need for more sophisticated communication methods emerged, leading to the development of written languages, semaphore systems, and other forms of coded communication.
Notable Milestones
- Ancient Egypt:Hieroglyphics, a system of written symbols, was developed around 3000 BCE, enabling the recording and transmission of complex information.
- Ancient Greece:The use of semaphore systems, using flags or torches to convey messages over long distances, was developed in the 5th century BCE.
- 19th Century:The invention of the telegraph and telephone revolutionized long-distance communication, allowing for the rapid transmission of messages across vast distances.
- 20th Century:The development of computers and digital technology led to the creation of new forms of coded communication, such as binary code and encryption algorithms.
Types of Signs, Signals, and Codes
Signs, signals, and codes come in a wide variety of forms, each designed to convey information in a specific context. Here are some common types:
Visual Signs
Visual signs are non-verbal cues that convey messages through sight. These include:
- Traffic signs:Regulate the flow of traffic and provide safety instructions.
- Road markings:Indicate lane boundaries, speed limits, and other road-related information.
- Body language:Non-verbal cues, such as gestures, facial expressions, and posture, that convey emotions and intentions.
Audio Signals
Audio signals are sounds that convey information. These include:
- Sirens:Emergency vehicles use sirens to alert other drivers and pedestrians.
- Horns:Vehicles use horns to communicate with other drivers, indicate their presence, or warn of danger.
- Morse code:A system of dots and dashes that represents letters and numbers, used for long-distance communication.
Written Codes
Written codes are systems of symbols that represent words or ideas. These include:
- Alphabets:Systems of letters that represent spoken sounds.
- Numerical codes:Systems of numbers that represent quantities or other information.
- Cipher codes:Secret codes that encrypt messages to prevent unauthorized access.
Digital Codes
Digital codes are systems of binary digits (0s and 1s) that represent information. These include:
- Binary code:The fundamental code used in computers to represent data.
- ASCII code:A code that represents characters as numbers, allowing computers to exchange text data.
- QR codes:Two-dimensional barcodes that store large amounts of information.
Methods for Sending and Receiving Signs, Signals, and Codes: Signs, Signals, And Codes Merit Badge

Various methods are employed to transmit and receive signs, signals, and codes, each with its own advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these techniques is crucial for effective communication.
Visual Methods
- Flags:Flags of different colors and patterns are waved to convey messages over short distances.
- Morse Code:A series of dots and dashes, represented by light flashes or audible beeps, is used to transmit messages.
- Smoke Signals:Smoke from fires is manipulated to create patterns that convey information.
- Heliographs:Mirrors are used to reflect sunlight in coded patterns, allowing for long-distance communication.
Audio Methods
- Whistles:Different whistle patterns can be used to signal messages.
- Sirens:Varying siren tones can convey specific alerts or instructions.
- Morse Code:Audible beeps or tones are used to transmit Morse Code messages.
Electronic Methods
- Telegraphs:Electrical signals are transmitted over wires to convey messages.
- Telephones:Voice signals are transmitted over wires or wirelessly to communicate.
- Radios:Electromagnetic waves are used to transmit voice, data, and images over long distances.
Applications of Signs, Signals, and Codes
Signs, signals, and codes play a vital role in communication, navigation, and safety across various fields. They provide standardized and efficient ways to convey information, guide actions, and ensure safety in diverse settings.
Communication
- Verbal Communication:Spoken and written language are examples of verbal signs that convey messages through words.
- Nonverbal Communication:Body language, gestures, and facial expressions are nonverbal signals that communicate emotions and intentions.
- Codes:Morse code, Braille, and semaphore are specialized codes used to transmit messages over long distances or in situations where verbal communication is not feasible.
Navigation
- Traffic Signs:Road signs, traffic lights, and pavement markings provide guidance and regulations for vehicles and pedestrians.
- Maritime Signals:Lighthouses, buoys, and flags are used to navigate ships at sea and communicate warnings and instructions.
- Aviation Signals:Runway lights, control tower instructions, and aircraft transponders ensure safe and efficient air travel.
Safety
- Emergency Signals:Fire alarms, smoke detectors, and distress beacons alert individuals to potential hazards and summon help.
- Hazard Signs:Warning labels, safety posters, and caution tape identify potential dangers and provide instructions for safe behavior.
- Medical Codes:Emergency medical technicians and doctors use standardized codes to communicate patient conditions and treatment plans.
Ethical Considerations in Using Signs, Signals, and Codes

The use of signs, signals, and codes carries ethical implications that require careful consideration. These tools have the potential to impact privacy, security, and even the course of history.
Privacy Concerns
The use of codes and signals can raise privacy concerns. Intercepting and deciphering these communications can lead to the unauthorized acquisition of sensitive information, including personal data, business secrets, or military intelligence.
Security Risks
The misuse of signs, signals, and codes can pose significant security risks. For example, malicious actors may use deceptive signals to mislead or confuse individuals or organizations, potentially leading to harm or financial loss.
Potential for Misuse
Signs, signals, and codes can also be used for malicious purposes, such as espionage, sabotage, or fraud. It is crucial to establish clear ethical guidelines and legal frameworks to prevent the misuse of these communication methods.
Skills and Knowledge Required for the Merit Badge
The Signs, Signals, and Codes merit badge requires Scouts to develop a comprehensive understanding of various communication methods beyond spoken language. To earn this badge, Scouts must demonstrate proficiency in recognizing, sending, and receiving different types of signs, signals, and codes.
The badge program emphasizes the importance of communication in various settings, including emergencies and outdoor adventures. Scouts will learn about the history, types, and applications of signs, signals, and codes, as well as the ethical considerations involved in their use.
Requirements
- Define signs, signals, and codes, and explain their historical significance.
- Identify and describe at least six different types of signs, signals, and codes, including their uses and limitations.
- Demonstrate proficiency in sending and receiving messages using at least three different methods, such as semaphore, Morse code, and hand signals.
- Explain the ethical considerations involved in using signs, signals, and codes, and discuss how to avoid misuse or misinterpretation.
- Develop a plan for using signs, signals, and codes in an emergency situation, and practice implementing it.
Activities
To earn the Signs, Signals, and Codes merit badge, Scouts will participate in various activities that reinforce the concepts and skills covered in the requirements. These activities may include:
- Attending a workshop or demonstration on different types of signs, signals, and codes.
- Practicing sending and receiving messages using semaphore, Morse code, and hand signals.
- Developing a communication plan for use in an emergency situation.
li>Participating in a simulated emergency scenario where they must use signs, signals, and codes to communicate.
Resources for Learning about Signs, Signals, and Codes
For further exploration of signs, signals, and codes, consider the following resources:
Books, Signs, signals, and codes merit badge
- The Code Book: The Science of Secrecy from Ancient Egypt to Quantum Cryptography by Simon Singh
- Semiotics: The Basics by Daniel Chandler
- Signs, Signals, and Codes: An Introduction to Semiotics by Umberto Eco
Websites
- Semiotics Online: https://www.aber.ac.uk/en/media/departments/cim/research/semiotics/
- International Association for Semiotic Studies: https://www.iass-ais.org/
- The Semiotic Society of America: https://www.semioticsociety.org/
Organizations
- The Semiotic Society of America
- The International Association for Semiotic Studies
- The Semiotics Association of Canada
These resources offer comprehensive and reliable information on various aspects of signs, signals, and codes, enabling further exploration and understanding of this fascinating field.
Final Thoughts

In the symphony of human communication, Signs, Signals, and Codes play an indispensable role, bridging the gaps between individuals, cultures, and even species. As we navigate the complexities of modern society, understanding and utilizing these tools effectively empower us to connect, collaborate, and navigate the world with clarity and purpose.
Clarifying Questions
What is the difference between a sign and a signal?
A sign is a naturally occurring event that conveys information, while a signal is a deliberately created event that carries a specific message.
What are some examples of codes used in everyday life?
Morse code, binary code, and traffic signs are all examples of codes commonly used in various contexts.
How can I earn the Signs, Signals, and Codes merit badge?
To earn this merit badge, you must demonstrate proficiency in sending and receiving messages using various signs, signals, and codes, as Artikeld in the official requirements.